Unraveling Accents: Northern Vs. Southern Pronunciation
Have you ever found yourself in a conversation, only to realize that a perfectly common word sounds completely different coming from someone else? This fascinating linguistic phenomenon is at the heart of understanding regional dialects, particularly when we delve into the intriguing world of northern words vs southern words pronunciation. From the bustling streets of New York to the charming bayous of Louisiana, or from the industrial North of England to the rolling hills of its South, the way we articulate sounds is a subtle yet powerful marker of our origin, creating a rich tapestry of English speech across the globe.
The distinctions between how people from different regions pronounce words can be quite stark, often leading to both amusement and occasional confusion among speakers. If you've ever wondered why certain words sound different among English speakers, or why a simple vowel can spark a debate, you're not alone. This article will explore some of the most controversial and noticeable pronunciation differences, offering insights into the linguistic tapestry that defines Northern and Southern accents in both American and British English. Keep reading to uncover the captivating nuances that shape our spoken language.
Table of Contents
- Why Do Accents Differ? The Roots of Regional Pronunciation
- The American Divide: Northern vs. Southern US English
- A Tale of Two Isles: Northern vs. Southern UK English
- More Than Just Sounds: Lexical and Semantic Differences
- Iconic Words: How Pronunciation Varies Across the Map
- The Dynamic Nature of Language: Accents in Flux
- Embracing Linguistic Diversity: Why These Differences Matter
- Navigating the Nuances: Tips for Understanding Regional Accents
Why Do Accents Differ? The Roots of Regional Pronunciation
The intricate mosaic of accents we hear today is not a random occurrence but the result of centuries of linguistic evolution, migration patterns, and social dynamics. Linguistically, differences in pronunciation, grammatical constructions, and how accents vary are deeply rooted in the region in which speakers live. When communities settle in distinct geographical areas, their language begins to evolve independently, influenced by factors such as isolation, contact with other languages, and internal linguistic shifts. For instance, the original settlers of a region might have brought a particular way of speaking from their homeland, and over generations, this way of speaking could either solidify or diverge further from other communities.
Consider the historical movements of people: waves of immigration, internal migration, and even geographical barriers like mountains or rivers can create linguistic islands where unique pronunciations develop and persist. These differences are often subtle, affecting vowel sounds, the emphasis on certain syllables, or the clarity of consonants. Over time, what starts as a minor variation can become a defining characteristic of a regional accent. The distinct patterns in northern words vs southern words pronunciation are a prime example of how these historical and social forces shape the very sounds we make, demonstrating language as a living, breathing entity constantly adapting to its environment and its speakers.
The American Divide: Northern vs. Southern US English
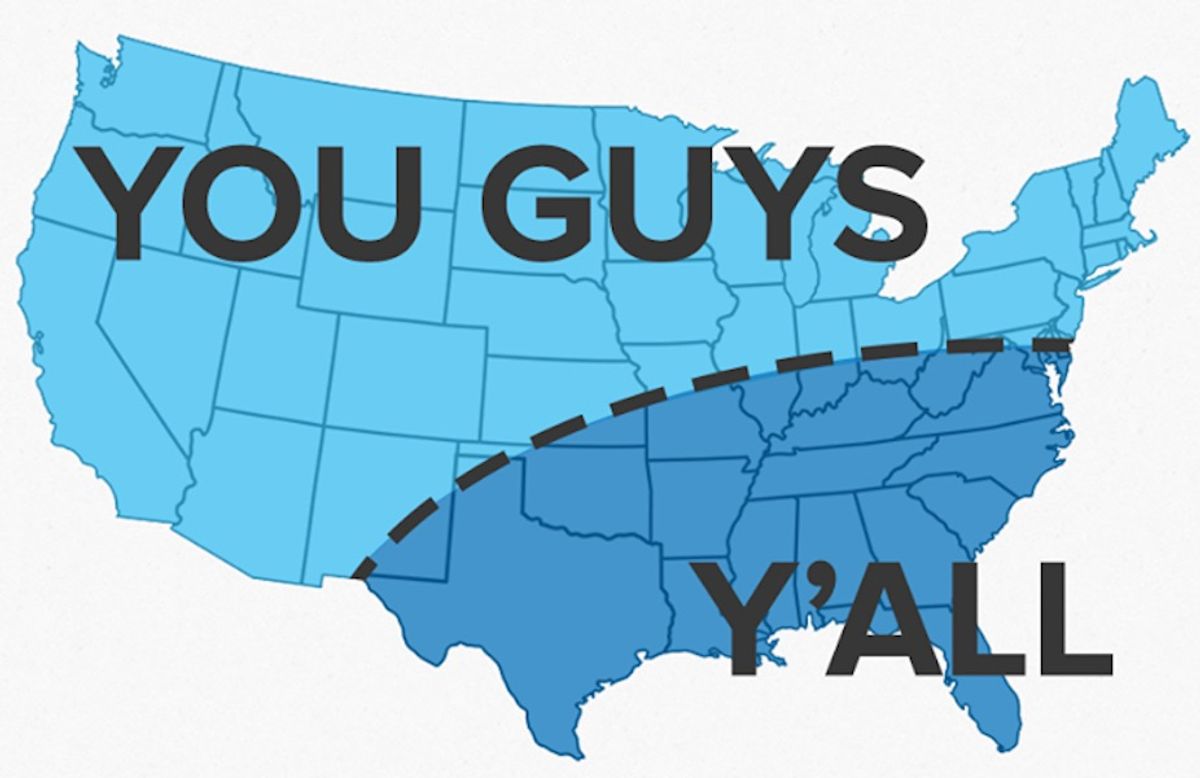
The United States, a vast nation, boasts an incredible array of regional accents, with the distinctions between Southern and Northern American English often being the most pronounced. These differences are not merely quaint local quirks; they represent deep-seated linguistic patterns that can be stark, leading to both confusion and amusement among speakers. When considering northern words vs southern words pronunciation in the US context, we're talking about a spectrum of sounds that range from the clipped, often rhotic accents of the Northeast and Midwest to the slower, more drawn-out vowels characteristic of the American South. This linguistic divergence has its roots in the settlement patterns of the early colonies and the subsequent westward expansion, where different groups of English speakers, often from varying regions of Britain, established distinct linguistic norms that have evolved independently for centuries.
For many, the "Southern drawl" is immediately recognizable, characterized by its unique vowel sounds and often slower pace, while Northern accents, particularly those from places like New York and the Midwest, feature clearer, more clipped vowel sounds. Here, the pronunciation of words is more concise, with less elongation. These differences extend beyond just a general impression, delving into specific phonetic shifts that define each region. Understanding these distinctions is key to appreciating the rich tapestry of American English, offering a glimpse into the diverse cultural heritage embedded within its spoken forms.
Vowel Vibrations: Key Pronunciation Differences in the US
When examining the heart of northern words vs southern words pronunciation in the US, vowels take center stage. One of the most notable differences is the pronunciation of certain vowel sounds, particularly the /aɪ/ diphthong, as in words like "my," "time," or "I." In the Southern United States, there is a strong tendency to pronounce the /aɪ/ sound as a monophthong, meaning it's reduced to a single, elongated vowel sound, often closer to "ah" or "ah-ee" without the distinct glide. So, "my" might sound more like "mah," and "time" like "tahm." This phenomenon, known as monophthongization, is a hallmark of many Southern accents.
In contrast, Northern accents, especially those in the Northeast and parts of the Midwest, typically maintain the diphthongal quality of /aɪ/, pronouncing it with two distinct parts, a clear glide from one vowel sound to another. For example, in New York or Boston, "my" retains its two-part sound. Another significant difference lies in the "cot-caught" merger. Many Northern and Western American accents have merged the vowel sound in "cot" (/ɑ/) and "caught" (/ɔ/), making them sound identical. However, in much of the South and some parts of the Northeast, these two vowel sounds remain distinct. So, while a Midwesterner might pronounce "Don" and "dawn" the same, a Southerner or a New Yorker would typically differentiate them. Furthermore, consider words like "route" or "roof." While Northeasterners might tend to pronounce "route" so it rhymes with "hoot," and some Midwesterners might pronounce it so it rhymes with "out," these variations highlight the regional diversity in how even common words are articulated, with just over 30 percent of respondents in some surveys showing these distinct preferences.
Consonants and R-Sounds: Beyond the Vowels
While vowels often grab the spotlight when discussing northern words vs southern words pronunciation, consonants and intonation patterns also play a crucial role in distinguishing American accents. One significant feature across most of the United States, both North and South, is rhoticity – the pronunciation of the 'r' sound after a vowel, as in "car" or "park." Unlike many non-rhotic British accents, most American accents generally pronounce this 'r'. However, subtle variations exist. For instance, in some parts of the South, particularly in older or more traditional accents, the 'r' sound might be less pronounced or even dropped in certain contexts, especially before consonants or at the end of words, creating a softer sound. Conversely, some Northern accents maintain a very strong, clear 'r' sound in all positions.
Beyond individual sounds, the rhythm and melody of speech, known as prosody or intonation, also differ. Southern accents are often characterized by a slower tempo and a more melodic, "sing-song" quality, with longer vowel durations and glides. Northern accents, particularly those from urban centers, tend to be more staccato, with words pronounced more concisely and vowel sounds being shorter and more clipped. These differences in rhythm and stress contribute significantly to the overall perception of an accent, making it immediately recognizable whether someone is from the North or the South. The combination of specific vowel shifts, subtle consonant variations, and distinct intonation patterns creates the rich and varied soundscapes of American English, making each regional accent a unique linguistic fingerprint.
A Tale of Two Isles: Northern vs. Southern UK English
Across the Atlantic, the United Kingdom presents its own fascinating dichotomy in regional speech, with the question of "what words are pronounced differently in the UK North and South?" being a frequent topic of discussion. One of the most noticeable differences in accent between the North and the South of England is indeed the pronunciation of words, creating a linguistic landscape as diverse as its geography. The "northern vs southern words UK" is a question that many people have asked, and this article will explore the differences between the two dialects and what they sound like to an outsider's ear. While Southern British English, particularly Received Pronunciation (RP), is often associated with a more "standard" or "posh" sound, Northern accents are incredibly varied, ranging from the distinct sounds of Liverpool (Scouse) and Manchester to the broader Yorkshire accents.
These differences are not just about a general 'sound' but are rooted in specific phonetic shifts that have occurred differently across the country over centuries. The historical development of English saw various sound changes spread unevenly, leading to the distinct vowel and consonant systems we hear today. For example, some sound changes that affected Southern English never reached the North, and vice versa. This has resulted in a fascinating divergence in how even very common words are articulated. Understanding these regional variations is crucial for anyone trying to grasp the full spectrum of British English, whether for communication, cultural appreciation, or even when learning a British accent, as these are some of the most important characteristics to know.
The Great Vowel Splits: TRAP-BATH and FOOT-STRUT
When delving into the specifics of northern words vs southern words pronunciation in the UK, two vowel distinctions stand out as particularly defining: the TRAP-BATH split and the FOOT-STRUT split. Have you heard of the TRAP-BATH split? This refers to words like "bath," "grass," "path," and "dance." In Southern British English (including RP), these words are typically pronounced with a long 'ah' sound, similar to the vowel in "father." So, "bath" sounds like "bahth." In contrast, most Northern English accents pronounce these words with a short 'a' sound, as in "trap" or "cat." Thus, "bath" sounds like "bath" with a short 'a', making it rhyme with "math." This is a clear and immediate marker of whether a speaker is from the North or the South.
Equally significant is the FOOT-STRUT split. This is the matter of the vowel in words like "strut," "cup" (and saucer), "love," and so on. In Southern English, these words use the 'ʌ' sound, as in "cut" or "but." However, in many Northern accents, particularly in parts of Lancashire and Yorkshire, the vowel in these words is pronounced with an 'ʊ' sound, similar to the vowel in "foot" or "put." As we all know, a typically Northern pronunciation would make "cup" sound more like "coop" (with the vowel from "foot"), and "love" might sound closer to "loov." These two vowel splits are fundamental characteristics you need to know when learning a British accent, as they are key phonetic differentiators that immediately signal a speaker's regional origin within the UK, showcasing the profound impact of these subtle vowel shifts on the overall sound of an accent.
More Than Just Sounds: Lexical and Semantic Differences
While the primary focus of northern words vs southern words pronunciation lies in how sounds are articulated, it's important to acknowledge that regional differences extend beyond phonetics to include variations in vocabulary and meaning. Some of the differences come from pronunciations, while some come from a regional dialect, where entirely different words are used for the same concept, or the same word carries different meanings. This fascinating aspect of language highlights how culture and geography shape our lexicon as much as our phonology.
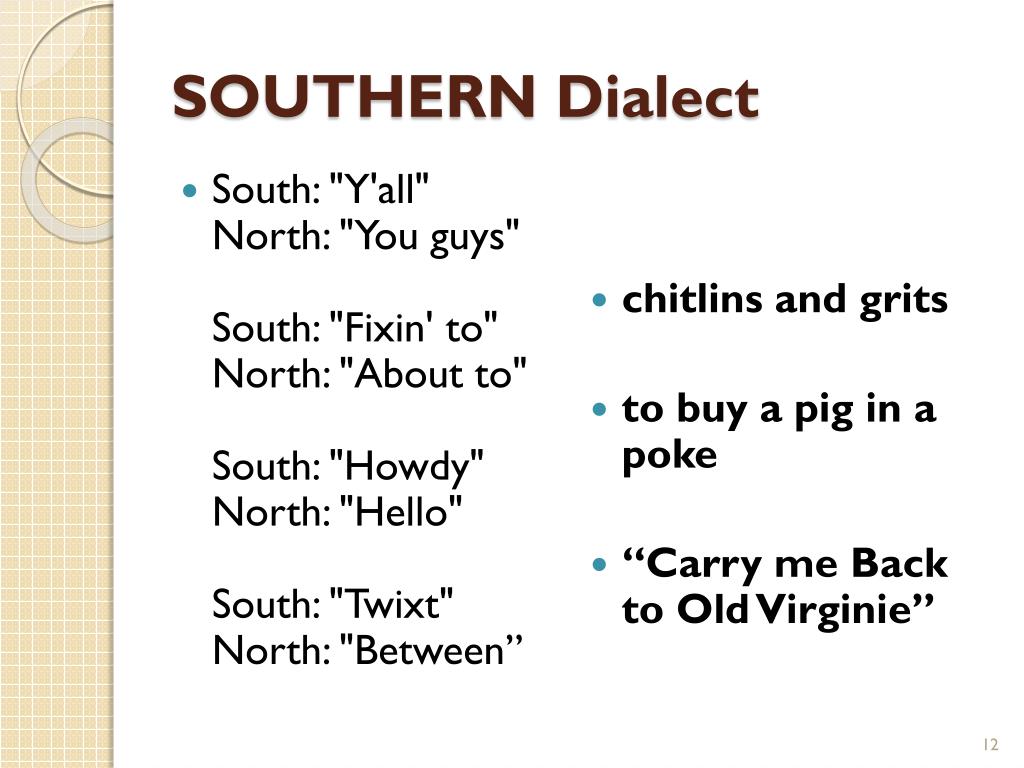
A classic American example of a word with different meanings is "Yankee." In the Northern US, particularly in New England, a "Yankee" is historically a New Englander. And in the South, a "Yankee" is a Northerner, often used to refer to anyone from the Union states during the Civil War, and suffice it to say, it is not always a loving term. This is one that the Midwest and the South can often agree on its broader, sometimes pejorative, meaning. This simple word perfectly illustrates how regional history and identity can imbue a term with entirely distinct connotations.
Similarly, in the UK, while the focus is often on pronunciation, there are also distinct lexical differences. For instance, in parts of the North, people might say "ginnel" for an alleyway, whereas in the South, it's typically "alley" or "passage." And if we look beyond English, to Welsh spoken in different regions of Wales, the differences can be even more pronounced: in the North they say "llefrith" for milk, whereas in the South they say "llaeth." Oh, and they say "rwan" for "now" whereas in the South they say "nawr." Certain terms are unique to the North or South, showcasing that language variation encompasses a rich tapestry of vocabulary, not just the sounds we make. This list gives a glimpse into how many words have different meanings or are entirely different across regions, adding another layer to the complexity and beauty of regional dialects.
Iconic Words: How Pronunciation Varies Across the Map
Beyond the systematic vowel shifts and lexical differences, there are numerous individual words whose pronunciations can spark immediate recognition of a speaker's regional origin. If you want to find out which words sound different among English speakers, we’ve got you covered with a list of words people say differently or pronounce differently across the US and UK. These are some of the controversial pronunciation differences that often lead to lively debates. For instance, consider the word "caramel." In many Northern American accents, it's often pronounced with two syllables, "car-mel," omitting the middle 'a' sound. In contrast, many Southern speakers, and indeed some from other regions, pronounce it with three distinct syllables: "care-uh-mel."
Another classic example is "pecan." In the South, it's commonly pronounced "pee-KAHN," with emphasis on the second syllable and a long 'ah' sound. Northerners, however, might opt for "PEE-can," with emphasis on the first syllable and a short 'a' sound. The word "aunt" also varies; in much of the US, it rhymes with "ant," but in parts of New England and some Southern accents, it can rhyme with "font" or "jaunt," using a broader 'ah' sound. They also show how Northerners and Southerners can pronounce the same words in completely different ways. In an example, ‘one’ and ‘gone’ typically rhyme when spoken by Northerners (both having the vowel sound of 'on'), but in some Southern accents, 'one' might retain a distinct vowel sound that doesn't rhyme with 'gone'.
Other common words that exhibit fascinating regional variations include "roof" (rhyming with "hoof" in some areas, "proof" in others), "data" (DAY-tuh vs. DAH-tuh), "crayon" (cray-ON vs. CRAY-uhn), and "mayonnaise" (MAY-uh-nayz vs. MAN-ayz). These examples, though seemingly minor, serve as powerful linguistic markers, instantly signaling a speaker's regional background and contributing to the rich diversity of English pronunciation. It's a testament to the dynamic nature of language that such common words can hold such varied phonetic identities across different regions.
The Dynamic Nature of Language: Accents in Flux
While we've explored the distinct characteristics of northern words vs southern words pronunciation, it's crucial to understand that language is not static; it's a living, breathing entity constantly evolving. Accents are not immune to change, influenced by factors such as globalization, media exposure, increased mobility, and social trends. There's a fascinating ongoing process of accent leveling, where regional distinctions can sometimes diminish over time, particularly in areas with high population movement or strong media influence. For instance, a new study predicts that people from the North of England could sound the same as people from the South by 2066. This research, published in the Journal of Physics, suggests that continuous interaction and the pervasive influence of media could lead to a homogenization of accents, particularly among younger generations.
However, it's also important to note that while some features may converge, others might diverge, and new regional variations can emerge. Language change is complex and multi-directional. The rise of social media and online communities, for example, can also foster the strengthening of certain regional identities or the spread of new linguistic innovations. The way we watch us say all the different ways to pronounce a word, whether through online videos or personal interactions, continuously shapes our linguistic landscape. So, while predictions about accent convergence are intriguing, the full picture of language evolution is always more nuanced, with regional accents likely to retain their unique charm and distinctiveness in various forms for the foreseeable future, even as they adapt to a changing world.
Embracing Linguistic Diversity: Why These Differences Matter
The variations in northern words vs southern words pronunciation are far more than mere curiosities; they are vital components of our cultural heritage and identity. Each accent tells a story – of history, migration, community, and individual experience. Embracing this linguistic diversity means recognizing the inherent value in every way of speaking, rather than imposing a single "correct" standard. These differences foster a rich tapestry of communication, making English a vibrant and endlessly fascinating language. They challenge us to listen more closely, to appreciate the nuances, and to understand that variety is a strength, not a weakness.
From a social perspective, acknowledging and respecting diverse pronunciations helps break down stereotypes and fosters greater understanding between people from different regions. It reminds us that language is a powerful tool for connection, even when the sounds themselves differ. Linguistically, these variations provide invaluable data for researchers studying how languages evolve, how sound changes occur, and how social factors influence speech patterns. They are living laboratories for understanding the human capacity for language. So, next time you hear a word pronounced differently, instead of correcting or judging, take a moment to appreciate the unique journey of that sound and the rich cultural story it carries.
Navigating the Nuances: Tips for Understanding Regional Accents
For
PPT - What is Accent v. Dialect? PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Word Usage: North VS. South

Southern Words: Learn This Unique Dialect to Understand People in the