Navigating Canada's Power: Your Essential Guide To Voltage & Plugs
**Table of Contents** * [Understanding Canada's Electrical Standard: The Core of "加拿大 電壓"](#understanding-canadas-electrical-standard-the-core-of-加拿大-電壓) * [Plug Types in Canada: A-Type and B-Type Explained](#plug-types-in-canada-a-type-and-b-type-explained) * [What's the Difference Between A-Type and B-Type Plugs?](#whats-the-difference-between-a-type-and-b-type-plugs) * [The Critical Importance of Voltage Compatibility](#the-critical-importance-of-voltage-compatibility) * [Devices from High-Voltage Countries (e.g., China, Hong Kong) in Canada](#devices-from-high-voltage-countries-eg-china-hong-kong-in-canada) * [Frequency Matters: 60Hz vs. 50Hz](#frequency-matters-60hz-vs-50hz) * [Essential Gear for Your Canadian Trip: Adapters and Converters](#essential-gear-for-your-canadian-trip-adapters-and-converters) * [Do I Need a Voltage Converter for My Device?](#do-i-need-a-voltage-converter-for-my-device) * [Safety First: Crucial Tips for Electrical Use in Canada](#safety-first-crucial-tips-for-electrical-use-in-canada) * [Beyond Voltage: A Glimpse into Canadian Life and Electrical Needs](#beyond-voltage-a-glimpse-into-canadian-life-and-electrical-needs) * [Powering Your Digital Life: From Rocky Mountains to Urban Hubs](#powering-your-digital-life-from-rocky-mountains-to-urban-hubs)
---
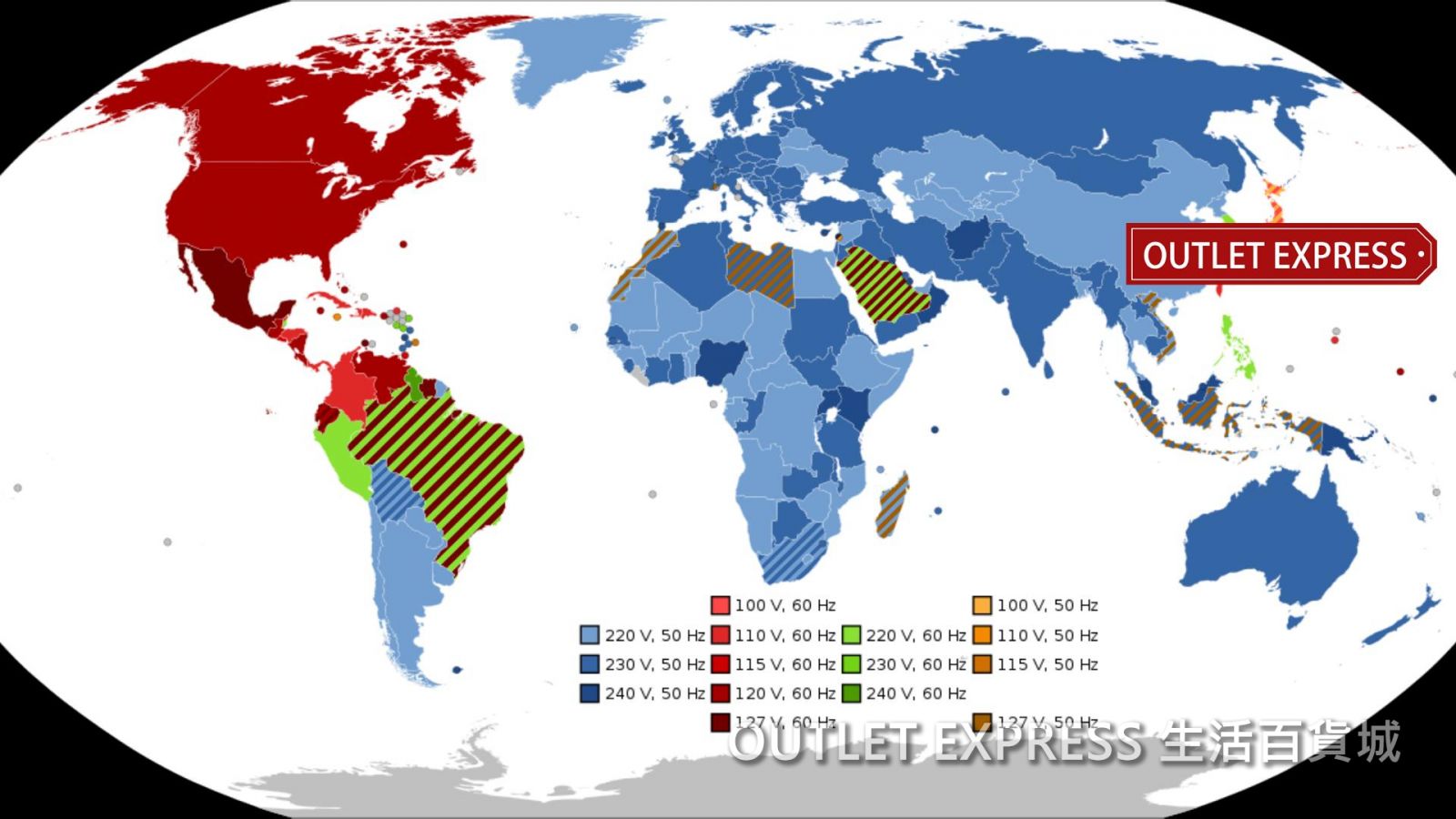
## Understanding Canada's Electrical Standard: The Core of "加拿大 電壓" When you travel internationally, one of the first things you'll notice upon trying to plug in your phone charger or laptop is that not all electrical outlets are created equal. This is particularly true when moving between continents or regions with different historical electrical infrastructure developments. For anyone planning a visit or a longer stay, grasping the specifics of **Canada voltage** is paramount. Canada, much like its neighbor to the south, the United States, operates on a specific electrical standard that differs significantly from many parts of the world, particularly Europe, Asia, and Australia. The standard voltage in Canada is **120 volts (V)**, and the frequency is **60 hertz (Hz)**. This is a crucial piece of information, as many countries, including China, Hong Kong, and most of Europe, use a voltage of 220V or 240V and a frequency of 50Hz. What does this mean for your devices? Simply put, if your device is designed to operate solely on 220V/50Hz, plugging it directly into a 120V/60Hz Canadian outlet without the proper equipment can lead to either non-functionality or, in some cases, damage. The lower voltage means less power is supplied, which can result in appliances like hair dryers not heating up sufficiently or not working at all. Conversely, if you were to take a device designed for 120V to a 220V country without a converter, it could overload and be permanently damaged, or even pose a fire risk. Therefore, understanding this fundamental difference in **Canada voltage** is the first step in ensuring a hassle-free electrical experience.
## Plug Types in Canada: A-Type and B-Type Explained Beyond just the voltage, the physical shape of the plug and the corresponding outlet also matters. You could have the correct voltage, but if your plug doesn't fit the socket, you're still out of luck. In Canada, you will primarily encounter two types of electrical plugs and outlets: **Type A** and **Type B**. These are the same types used across North America, making travel between Canada and the United States electrically seamless in terms of plug shape. * **Type A Plug:** This is the simpler of the two, featuring **two flat parallel blades**. It's commonly used for smaller, ungrounded appliances like phone chargers, lamps, or small electronics that don't require a ground connection for safety. While widely used, it's important to note that Type A plugs do not offer the same level of electrical safety as Type B, as they lack a grounding pin. * **Type B Plug:** This plug is easily identifiable by its **two flat parallel blades and an additional round or U-shaped grounding pin** located below the two flat blades. The grounding pin provides an extra layer of safety by diverting excess electrical current directly into the ground, preventing electric shocks in case of a fault. Most modern appliances, especially those with metal casings or higher power requirements (like laptops, kitchen appliances, or power tools), are designed with Type B plugs for enhanced safety. When preparing for your trip, it's crucial to check the plugs on all your electronic devices. If they don't match Type A or Type B, you will need a **plug adapter**. This adapter doesn't change the voltage; it merely changes the physical configuration of your plug so it can fit into a Canadian outlet.
### What's the Difference Between A-Type and B-Type Plugs? The fundamental difference between Type A and Type B plugs lies in the presence of a grounding pin. Type A is ungrounded, meaning it only has the two active prongs that carry the current. Type B, on the other hand, includes a third, round or U-shaped prong specifically for grounding. This grounding pin is a critical safety feature. In the event of an electrical fault within an appliance (for example, if a live wire touches the metal casing), the grounding pin provides a safe path for the electricity to flow directly to the earth, tripping a circuit breaker and preventing the user from receiving an electric shock. While a Type A plug can often fit into a Type B outlet (as the two flat blades are compatible), a Type B plug cannot fit into a Type A outlet due to the missing hole for the grounding pin. For travelers, this means that if your device has a Type B plug, you must ensure your adapter and the Canadian outlet you plan to use are also Type B compatible, or at least accommodate the grounding pin. Always prioritize using grounded connections (Type B) for appliances that come with them, as this is how they are designed to be used safely. Understanding these plug types is just as vital as knowing the **Canada voltage** for a secure electrical experience.
## The Critical Importance of Voltage Compatibility Imagine arriving in the beautiful Banff National Park, ready to capture the stunning vistas of Lake Louise, only to find your camera battery charger won't work. Or perhaps you're a student enrolled in a DLI (Designated Learning Institution) in Vancouver, and your laptop, essential for your studies, refuses to power on. These frustrating scenarios are often a direct result of voltage incompatibility. The phrase "用錯電壓會怎樣" (what happens if you use the wrong voltage) perfectly encapsulates the potential pitfalls. Using an appliance with the wrong voltage can lead to a range of issues, from mere inconvenience to serious safety hazards: * **Under-voltage (Device from High-Voltage Country in Canada):** If you bring a device designed for 220V (like many from China or Hong Kong) and plug it into a 120V Canadian outlet without a voltage converter, the device will receive less power than it needs. * **Symptoms:** The device might not work at all, or it might function very poorly. For example, a 220V hair dryer will not produce enough heat, or a motor might run sluggishly. While it might seem less dangerous than over-voltage, prolonged under-voltage use can still stress the device's components and shorten its lifespan. * **Example from Data:** "例如使用電風筒會不能發熱,皆因裝置本身要用 220v 電壓,但到日本等只有 100v 電壓的地方使用,就..." (for example, a hair dryer won't heat up because the device itself needs 220v, but when used in places like Japan which only have 100v, it will...). This perfectly illustrates the effect of insufficient voltage. * **Over-voltage (Device from Low-Voltage Country in High-Voltage Country):** This is the more dangerous scenario, though less likely if you're bringing Canadian devices abroad. If a 120V device is plugged into a 220V outlet without a converter, it will receive double the voltage it's designed for. * **Symptoms:** This can cause immediate and severe damage to the device's internal components, leading to overheating, smoke, or even fire. The device could be permanently destroyed. The key takeaway here is that voltage compatibility is not just about whether your device works, but also about safety and the longevity of your electronics. Always check the input voltage range on your device's power adapter or label before plugging it in. This is why understanding **Canada voltage** is a critical piece of information for any international visitor or new resident.
### Devices from High-Voltage Countries (e.g., China, Hong Kong) in Canada Many travelers and new immigrants to Canada come from regions where 220V or 240V is the standard, such as China, Hong Kong, or European countries. Bringing electronics from these regions to Canada's 120V system requires careful consideration. As noted in the provided data: "中加兩國相互使用電器嗎,會不會因為電壓差異而產生問題呢? 如果高電壓電器帶到低電壓的國家去,如中國用220v的電器帶到加拿大110v的環境下,一般情況下是可以勉強使用,但往..." (Can electrical appliances from China and Canada be used interchangeably, will there be problems due to voltage differences? If a high-voltage appliance is brought to a low-voltage country, such as a 220V Chinese appliance brought to a 110V Canadian environment, generally it can be barely used, but...). This statement highlights a common misconception and a potential risk. While some very basic, non-motorized, or resistive appliances (like a simple heating coil) might "barely work" at half their intended voltage, their performance will be severely compromised, and they might still be damaged over time. For sensitive electronics, motors, or heating elements, this simply isn't an acceptable solution. For example, a Japanese rice cooker designed for 100V might "work" in Canada's 110V/120V system because the voltage difference is minimal and often within the acceptable tolerance range for such appliances, as indicated by the data: "日本電飯鍋100v的電壓,拿到加拿大(電壓110v)可以正常使用嗎?需要變壓器嗎? 4樓:匿名使用者. 只要電源插座通用就可以用,不需要變壓器!100v電壓實際上的適用範圍為100-110v." This suggests a small variance is often fine. However, a jump from 220V to 120V is a significant drop and almost always necessitates a voltage converter or transformer to ensure proper and safe operation. Ignoring this can lead to disappointment, damaged goods, or even safety hazards, emphasizing the importance of understanding **Canada voltage** and taking appropriate precautions.
## Frequency Matters: 60Hz vs. 50Hz While voltage often gets the most attention, the electrical frequency (measured in Hertz, Hz) is another critical factor to consider when using international electronics in Canada. Canada operates on a **60Hz** frequency, which is different from the **50Hz** standard used in many parts of the world, including Europe, Asia, and Africa. What exactly is frequency? It refers to the number of times per second that the alternating current (AC) changes direction. This might sound highly technical, but for certain types of appliances, it can make a noticeable difference: * **Motorized Appliances:** Devices that rely on motors, such as fans, hair dryers (especially those with powerful motors), electric clocks, or some kitchen appliances, can be affected by frequency differences. A 50Hz motor running on a 60Hz supply might run slightly faster than intended, potentially causing premature wear or overheating. Conversely, a 60Hz motor on a 50Hz supply might run slower and less efficiently. * **Timing Devices:** Old-fashioned electric clocks or timers that rely on the AC frequency for accurate timekeeping will run incorrectly if the frequency is different. A 50Hz clock on a 60Hz supply will run fast, while a 60Hz clock on a 50Hz supply will run slow. * **Heating Elements and Resistive Loads:** For simple heating appliances like kettles, irons, or basic resistive heaters, the frequency difference is usually negligible. Their operation primarily depends on the voltage. * **Modern Electronics:** Fortunately, most modern electronic devices like laptops, phone chargers, cameras, and tablets are designed with "switching power supplies" that can automatically adapt to both 50Hz and 60Hz frequencies, as long as the voltage is within their specified range (e.g., "Input: 100-240V, 50/60Hz"). Always check the label on your device or its power adapter. While the frequency difference is less likely to cause immediate damage compared to a significant voltage mismatch, it's still an important consideration for optimal performance and longevity of certain appliances. When assessing your electrical needs for **Canada voltage**, don't forget to glance at the frequency specification on your devices.
## Essential Gear for Your Canadian Trip: Adapters and Converters Now that we've covered the specifics of **Canada voltage**, frequency, and plug types, let's talk about the practical solutions for ensuring your devices work flawlessly: plug adapters and voltage converters. These two pieces of equipment are often confused, but they serve very different, yet equally crucial, purposes. * **Plug Adapter:** A plug adapter is a simple device that physically changes the shape of your appliance's plug to fit into a different type of wall socket. It does **not** change the voltage or frequency. If your device is "dual voltage" (meaning it can accept a range of voltages, e.g., 100V-240V) and you're coming from a country with different plug shapes, a plug adapter is all you'll need. For instance, if you're traveling from the UK (Type G plug) to Canada (Type A/B plug) with a dual-voltage laptop charger, a simple plug adapter will suffice. * **Voltage Converter (or Transformer):** A voltage converter is a more complex device that actually changes the electrical voltage from one level to another. If your appliance is *not* dual voltage and is designed for a higher voltage (e.g., 220V) than Canada's 120V, you will need a voltage converter to step down the voltage. Conversely, if you're taking a 120V Canadian device to a 220V country, you'd need a step-up converter. Converters are typically larger and heavier than simple plug adapters and are essential for high-power appliances like hair dryers, curling irons, or certain kitchen appliances that are not dual voltage. Many travelers opt for a **universal travel adapter with built-in voltage conversion capabilities**. These all-in-one devices can be incredibly convenient, offering multiple plug configurations and often a voltage conversion function. However, always check the power rating (wattage) of the converter to ensure it can handle your appliance's power consumption. Overloading a converter can damage both the converter and your appliance.
### Do I Need a Voltage Converter for My Device? Determining whether you need a voltage converter is straightforward: 1. **Check Your Device's Label/Power Adapter:** Look for the "Input" specifications. * **"Input: 100-240V, 50/60Hz"**: If you see this, your device is "dual voltage" or "multi-voltage." It can safely operate on any voltage between 100V and 240V and adapt to both 50Hz and 60Hz frequencies. This means you only need a **plug adapter** to physically fit it into a Canadian outlet. Most modern laptops, phone chargers, camera chargers, and many travel-specific appliances fall into this category. * **"Input: 220-240V, 50Hz"** (or similar, indicating a single voltage range not including 120V): If your device specifies a single voltage range that does not include 120V (e.g., only 220V, or only 230V), then you **will need a voltage converter** to step down the 220V to Canada's 120V. This is common for high-power appliances like hair dryers, electric kettles, or older electronic devices. Remember, the goal is to match the power requirements of your device with the supply in Canada. Failing to do so can be costly and potentially dangerous. Investing in the right adapter and converter is a small price to pay for peace of mind and fully functional electronics during your Canadian adventure.
## Safety First: Crucial Tips for Electrical Use in Canada Beyond simply ensuring your devices work, electrical safety is paramount. Mishandling electricity can lead to serious injury, fire, or damage to property. The provided data includes excellent safety tips that bear repeating and expanding upon. When dealing with **Canada voltage** and any electrical appliances, always prioritize safety: 1. **Do Not Overload Outlets:** Each electrical outlet and circuit has a maximum current capacity. Plugging too many high-power devices into a single outlet or power strip can draw more current than the circuit is designed to handle, leading to tripped circuit breakers, overheating, and a significant risk of fire. Use common sense and distribute your appliances across different outlets if possible. 2. **Do Not Use Damaged Cords or Appliances:** Frayed wires, cracked insulation, bent or loose prongs, or any visible damage to an appliance's cord or casing are red flags. Damaged electrical components can expose live wires, leading to electric shock or short circuits. Immediately discontinue use of any damaged electrical item and have it repaired by a qualified professional or replace it. 3. **Do Not Use Appliances in Wet Places:** Water and electricity are a dangerous combination. Never use electrical appliances near sinks, bathtubs, showers, or in any damp environment. Even residual moisture can conduct electricity and cause severe shocks. This is especially true for bathrooms, where outlets are often GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter) protected, but caution is still essential. 4. **If You Touch Electricity, Seek Medical Help Immediately:** In the unfortunate event of an electric shock, even if it seems minor, seek medical attention immediately. Electrical shocks can cause internal damage, including heart rhythm disturbances, that may not be immediately apparent. 5. **Always Use Grounded Connections When Available:** As discussed with Type B plugs, the grounding pin is a critical safety feature. If your device has a three-prong plug, always use a three-prong adapter and plug it into a grounded (Type B) outlet. Never remove or bend the grounding pin to force a three-prong plug into a two-prong outlet. This defeats the safety purpose and can be extremely dangerous. 6. **Purchase Certified Products:** When buying adapters, converters, or any electrical accessories, ensure they are certified by recognized safety standards organizations. In Canada, look for certifications like CSA (Canadian Standards Association) or UL (Underwriters Laboratories) marks. These indicate that the product has been tested and meets safety requirements. 7. **Unplug When Not in Use:** For safety and energy conservation, unplug appliances when they are not in use, especially high-power items or chargers once devices are fully charged. By following these fundamental safety guidelines, you can minimize risks and enjoy a safe and worry-free experience with **Canada voltage** and your electronic devices.
## Beyond Voltage: A Glimpse into Canadian Life and Electrical Needs While understanding **Canada voltage** is crucial for practical purposes, it's also interesting to briefly connect it to the broader context of Canadian life. Canada is a vast and diverse country, known for its natural beauty, multicultural cities, and a distinct way of life that often influences how people use and rely on their electrical devices. For instance, the data mentions that "加拿大沒有加班文化,所以一到了周末假期,加拿大人不是去公園就或者去湖邊坐著" (Canada has no overtime culture, so on weekends and holidays, Canadians either go to parks or sit by the lake). This emphasis on work-life balance and outdoor activities means that devices like portable chargers, cameras, and perhaps even portable speakers become essential for enjoying weekends in places like the Rocky Mountains or by one of Canada's many lakes. Ensuring these devices are charged and ready requires a reliable power source, underscoring the importance of knowing your **Canada voltage** compatibility. Canada's population is also evolving. According to Statistics Canada, by 2031, visible minorities will constitute one-third of the total population, with Asian communities already reaching that figure in cities like Vancouver. This demographic shift means a growing number of residents and visitors from countries with different electrical standards, making the topic of voltage compatibility even more relevant for a diverse population. Furthermore, the data touches upon immigration and residency: "加拿大实行落地生国籍政策,加拿大入境最轻松的方式就是到加拿大生子。宝宝在加拿大出生就能自动拥有加拿大国籍,成为加拿大公民,继而可以为父母申请枫叶卡,帮父母拿到在加拿大的永居权。" (Canada implements birthright citizenship. The easiest way to enter Canada is to give birth in Canada. A baby born in Canada automatically acquires Canadian citizenship, becoming a Canadian citizen, and can then apply for a maple leaf card for their parents, helping parents obtain permanent residency in Canada). For those considering long-term stays or immigration, understanding the electrical system becomes part of settling in and establishing a comfortable home. Even daily habits are mentioned: "很多加拿大人一輩子都租房子,開二手車。" (Many Canadians rent houses for life and drive second-hand cars.) This practical approach to life extends to how people manage their belongings, including electronics. Being able to use existing devices from home, or confidently purchasing new ones, relies on a clear understanding of the local electrical standards.
### Powering Your Digital Life: From Rocky Mountains to Urban Hubs Whether you're chasing the aurora borealis, exploring the vibrant streets of Vancouver, or studying at a Designated Learning Institution, your digital devices are integral to your experience. From navigating with GPS to staying connected with loved ones, or simply powering your laptop for remote work or study, reliable electricity is non-negotiable. The economic landscape of Canada, much like other developed nations, is robust. Yet, the daily lives of Canadians often involve practical choices. For instance, "加拿大那个苦寒之地一点儿都不适合中老年人养老(温哥华可能好一点),就一个,整出心脑血管病怎么办?那是要命的。而且即使不是要命的,也会很痛苦,同时照顾老人也会很麻烦。把父母接到加拿大." (That bitterly cold place in Canada is not suitable for middle-aged and elderly people to retire (Vancouver might be better). What if they develop cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases? That's life-threatening. Even if not life-threatening, it will be very painful, and caring for the elderly will also be very troublesome. Bringing parents to Canada...). While this snippet highlights concerns about the elderly and health in colder regions, it indirectly points to the need for reliable power for medical devices, heating, and communication, which are vital for comfort and safety, especially for vulnerable populations. Ultimately, from a quick trip to see the classic sights of Banff and Lake Louise (where car parking is expensive, making shuttle buses a popular choice, meaning you'll want your phone charged for tickets and photos) to a long-term stay, your interaction with **Canada voltage** will be constant. Being prepared means you can focus on enjoying Canada's vast landscapes and unique culture, rather than worrying about a dead battery or a fried appliance.
## Conclusion Understanding **Canada voltage** and its associated electrical standards is far more than just a technical detail; it's a fundamental aspect of ensuring a safe, convenient, and enjoyable experience for anyone visiting or residing in Canada. We've explored that Canada operates on a

加拿大旅行必知:加拿大電壓是多少?加拿大插座是哪種?Skyscanner整理詳細加拿大電壓及插座資訊 - Skyscanner台灣 加拿大旅行

國際電壓|香港/台灣/日本/泰國/韓國/加拿大電壓、旅行轉插/插頭類型一覽 | ezone
OE生活小百科: 旅行電壓問題 不同國家的電壓及電器的合適電壓 - Outlet Express HK 生活百貨城